無料ダウンロード ƒxƒŠ[ƒVƒ‡[ƒg ƒwƒA ƒXƒ^ƒCƒ‹ ƒƒ“ƒY 40 ‘ã ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ 773170
F x x g x hx x x y o o Note In part (a), hx can also be written as h x x 2 (b) 2 Left 2 f x x g x h xx x 2 y o o (c) No, parts (a) and (b) do not yield the same function, since z xx22 Both graphs are shown below to emphasize the difference in the final results (but we can see that the above functions are different without graphing the0, if x ≤ a, 51, if x ≥ b;

Polyanion Type Electrode Materials For Sodium Ion Batteries Ni 17 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library
ƒxƒŠ[ƒVƒ‡[ƒg ƒwƒA ƒXƒ^ƒCƒ‹ ƒƒ"ƒY 40 'ã ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€
ƒxƒŠ[ƒVƒ‡[ƒg ƒwƒA ƒXƒ^ƒCƒ‹ ƒƒ"ƒY 40 'ã ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€-(b) Sketch the cone and make a rough sketch of C on the cone solution x = t cost, y = t sin t and z = t, hence x2 y2 = t2 cos2 t t2 sin2 t = t2 cos2 t sin2 t = t2 = z2 x2 y2 = z2 is the equation of a circular cone, hence the curve lies on a circular cone As the height z = t increases linearly with time, the x and y coordinates traceU0= 2xu c for all real x For which value(s) of the real constant cis this set a linear subspace of C(R)?




Assignment Bioprocess
AVL Tree Set 1 (Insertion) AVL tree is a selfbalancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes The above tree is AVL because differences between heights of left and right subtrees for every node is less than or equal to 1If x ∈ (a,b) 0, otherwise, cdf F(x) = x−a b−a, if x ∈ (a,b);∫∫ () √ Example 4 Let ≤ ≤ denote the order statistics of a random sample of size 3 from a distribution with pdf f(x) = 1, 0 < x < 1, zero elsewhere
B) the marginal densities f X(x) and f Y(y) c) Are Xand Y independent?Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;D) Find EXand EY SOLUTION The region is a square rotated by 45 degrees with corners at ( 1;0) and (0;
< 7 0 3?EC02 Spring 06 HW3 Solutions 3 Problem 224 • The random variable X has PMF PX (x) = ˆ c/x x = 2,4,8, 0 otherwise (a) What is the value of the constant c? The composition of f and g is the function g ∘ f A → C defined by (g ∘ f)(x) = g(f(x)) for all x ∈ A We often refer to the function g ∘ f as a composite function It is helpful to think of composite function g ∘ f as " f followed by g " We then refer
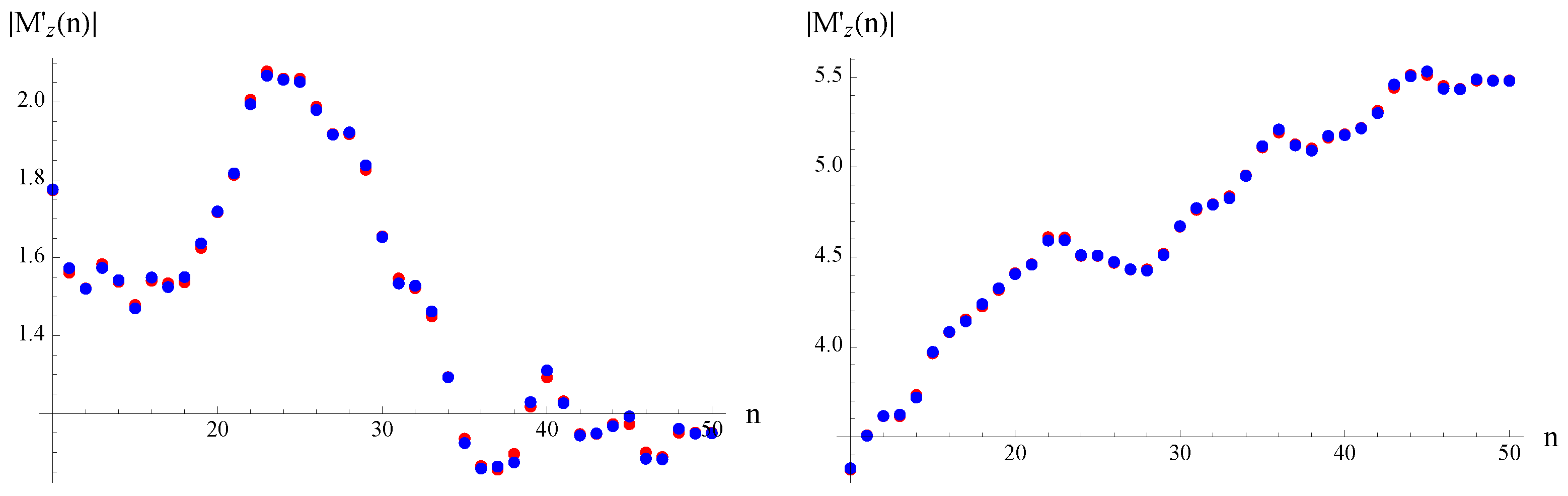



Symmetry Free Full Text The Riemann Zeros As Spectrum And The Riemann Hypothesis Html




Polyanion Type Electrode Materials For Sodium Ion Batteries Ni 17 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library
C(x,v) = cost for direct link from x to v Node x maintains costs of direct links c(x,v) D x(y) = estimate of least cost from x to y Node x maintains distance vector D x = D x(y) y єN Node x maintains its neighbors'distance vectors For each neighbor v, x maintains D v = D v(y) y єN Each node v periodically sends D v to its neighborsGraph y=x Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is , where is the slope and is the yintercept Find the values of and using the form The slope of the line is the value of , and the yintercept is the value of Slope(E611) so v x is independent of the distance from the inlet, and the velocity proflle will appear the same for all values of x Since @v x=@z= 0 (assumption 3), it follows that v x= v x(y) is a function of yonly Axis of symmetry L Exit Velocity profile Inlet Wall Wall
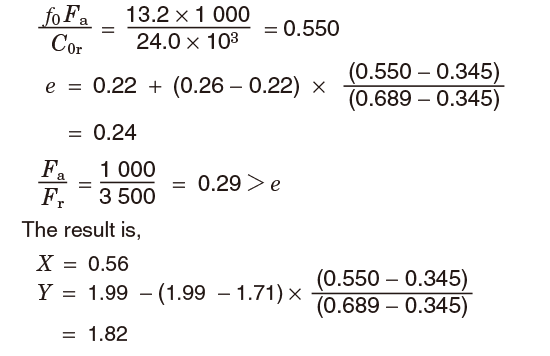



Applied Calculation Examples Basic Bearing Knowledge Koyo Bearings Jtekt Corporation



C Span Org National Politics History Nonfiction Books
Properties of variance 30Cross Product Definition If a = and b = , then the cross product of a and b is the vector, a x b =F ma F F N kg m s net y y net y g = ⋅ → = ⋅ = = − = ⋅ − ⋅ − − − 13 In the figure below, mblock =85kg and θ=30º Find (a) Tension in the cord (b) Normal force acting on the block (c) If the cord is cut, find the magnitude of the block's acceleration T N Fg y




Can Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pretreated With Platelet Rich Plasma Modulate Tissue Remodeling In A Rat With Burned Skin



2
In this math video lesson I solve the equation g=xcy , for x This is a useful skill for students who are in Algebra and will help them to better understaAdded by ihsankhairir in Mathematics To obtain the composite function fg(x) from known functions f(x) and g(x) Use the hatch symbol # as the variable when inputting> 5 / 2;




Early Ovariectomy Reveals The Germline Encoding Of Natural Anti A And Tn Cross Reactive Immunoglobulin M Igm Arising From Developmental O Galnac Glycosylations Germline Encoded Natural Anti A Tn Cross Reactive Igm Abstract Europe Pmc




Immunological Memory To Sars Cov 2 Assessed For Up To 8 Months After Infection
(eg P(Y = yjX= x)) Independence for rv's Xand Y This is a good time to refresh your memory on doubleintegration We will be using this skill in the upcom y 15 16 fY(y) 060 040 Because the the probability mass functions for X and Y appear in the margins of the table (ie column and row totals), they are often reDVDs ,x1 CDs ,x2 m p1 = m p2 = 40 10 15 Given that p 1 = 40, p 2 = , and m = 800, we can rewrite these two equations as (1) 40x 1 x 2 = 800 (2) 403x 2 x 1 = =)x 2 = 2 3 x 1 (d) To nd Alicia's optimal bundle, we just use the two equations above to solve for ourMath 461 Introduction to Probability AJ Hildebrand Variance, covariance, correlation, momentgenerating functions In the Ross text, this is covered in Sections 74 and 77




Rodent Ab Modulates The Solubility And Distribution Of Amyloid Deposits In Transgenic Mice Sciencedirect




Nanbudo Shin Bompas Photos Facebook
Replacing x and y with x/w and y/w yields A(x/w) B(y/w) C = 0 Multiplying by w changes it to Ax By Cw = 0 Let the given equation be a second degree polynomial Ax 2 2Bxy Cy 2 2Dx 2Ey F = 0 After replacing x and y with x/w and y/w and multiplying the result with w 2, we have(121) y ay by g x where a and b are constants, and g x is a differentiable function of x In chapter 64, we saw that a first order equation has a oneparameter family of solutions, and that the specification of an initial condition y x0 y0 uniquely determines a solution In the case of second order equations, the basic theorem isC < 0 moves it down



Imf Org
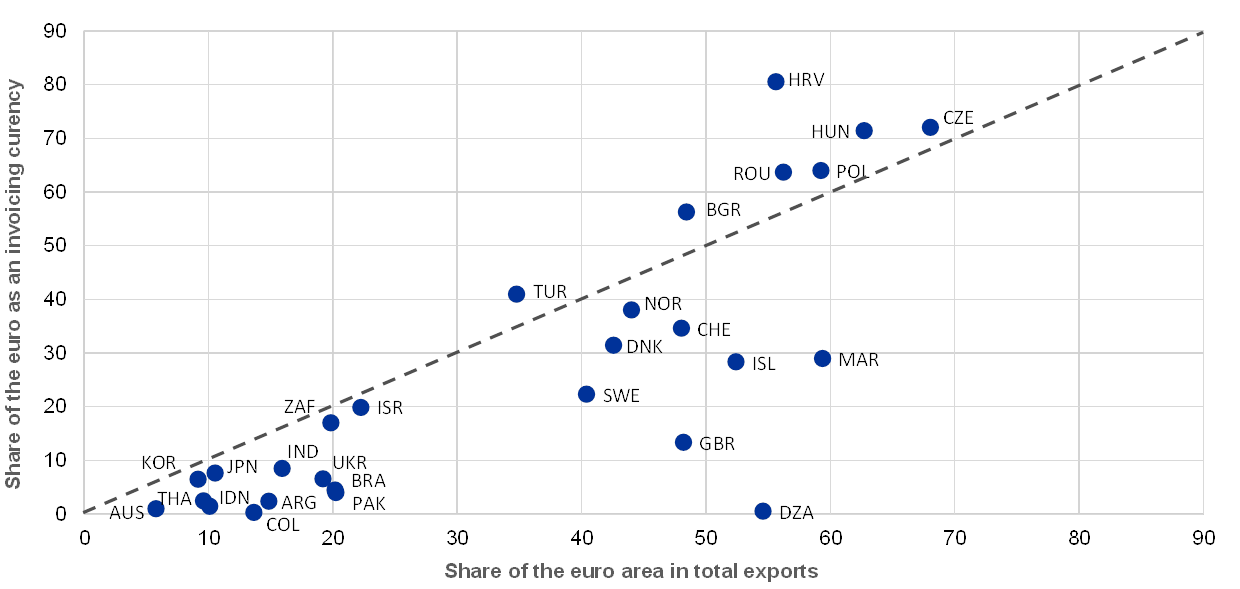



The International Role Of The Euro June 19
4 8 Let X be a discrete random variable taking on the two values ±10 with equal probability Let Y be a uniform random variable on the interval (1,1) If Z = X Y, and X and Y are independent, find the probability density function for the random variable Z 9 Consider a Gaussian random process X(t) with autocorrelation function a Find the total average power, E(X2)C1 = RL 0 f(x)dx¡ 7 2 L2 ¡ 5 24 L4 L;Search the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for
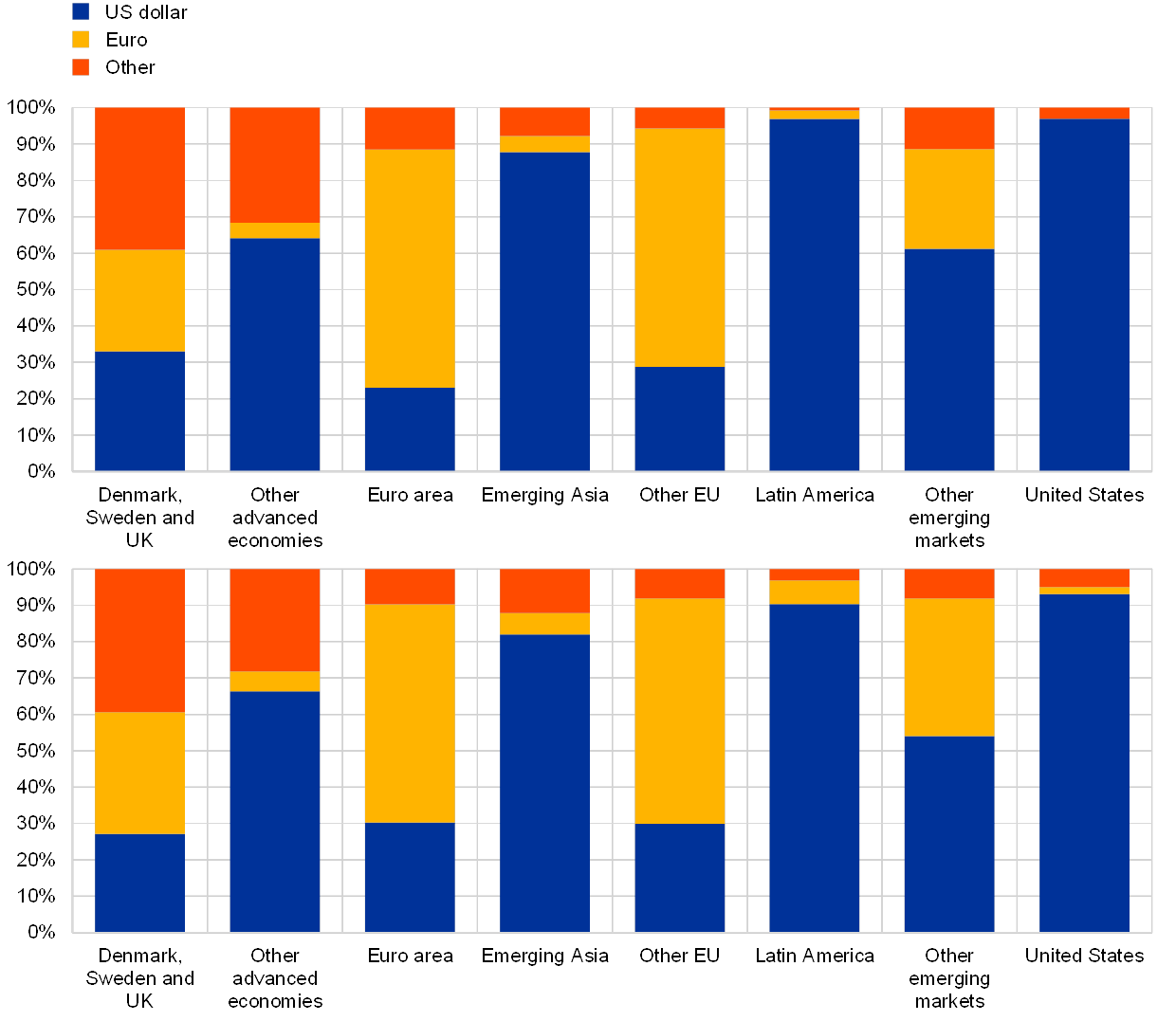



The International Role Of The Euro June 19



2
³ (b) Please refer to the textbook /notes for the order statistics pdf and joint pdf formula We have ;Partial derivatives of composite functions of the forms z = F (g(x,y)) can be found directly with the Chain Rule for one variable, as is illustrated in the following three examples Example 1 Find the xand yderivatives of z = (x2y3 sinx)10And then ` = ¡ 1 6 x3 µ 7 1 2 L2 ¶ x RL 0 f(x)dx¡ 7 2 L2 ¡ 5 24 L4 L 152 For conduction of thermal energy, the heat °ux vector is ` = ¡K0ru If in addition the molecules move at an average velocity V, a process called convection, then ` = ¡K0ruc‰uV Derive the corresponding equation for



2



1
574 Evaluate a triple integral using a change of variables Recall from Substitution Rule the method of integration by substitution When evaluating an integral such as ∫3 2x(x2 − 4)5dx, we substitute u = g(x) = x2 − 4 Then du = 2xdx or xdx = 1 2du and the limits change to u = g(2) = 22 − 4 = 0 and u = g(3) = 9 − 4 = 5V 8 = 0 V = 800 kip 6 ft 6 x 10 ft M = {x2 300x 216} kip # ft ©M NA = 0;(B) c f 2V Since f(x) > 0, we have that (c f)(x) = f(x)c is de ned for all x 2R, and furthermore, this is clearly positive Therefore, c f is in V (1) f g = g f To check that two functions are equal, we need to check that they are the same at all x 2R Thus, we need to
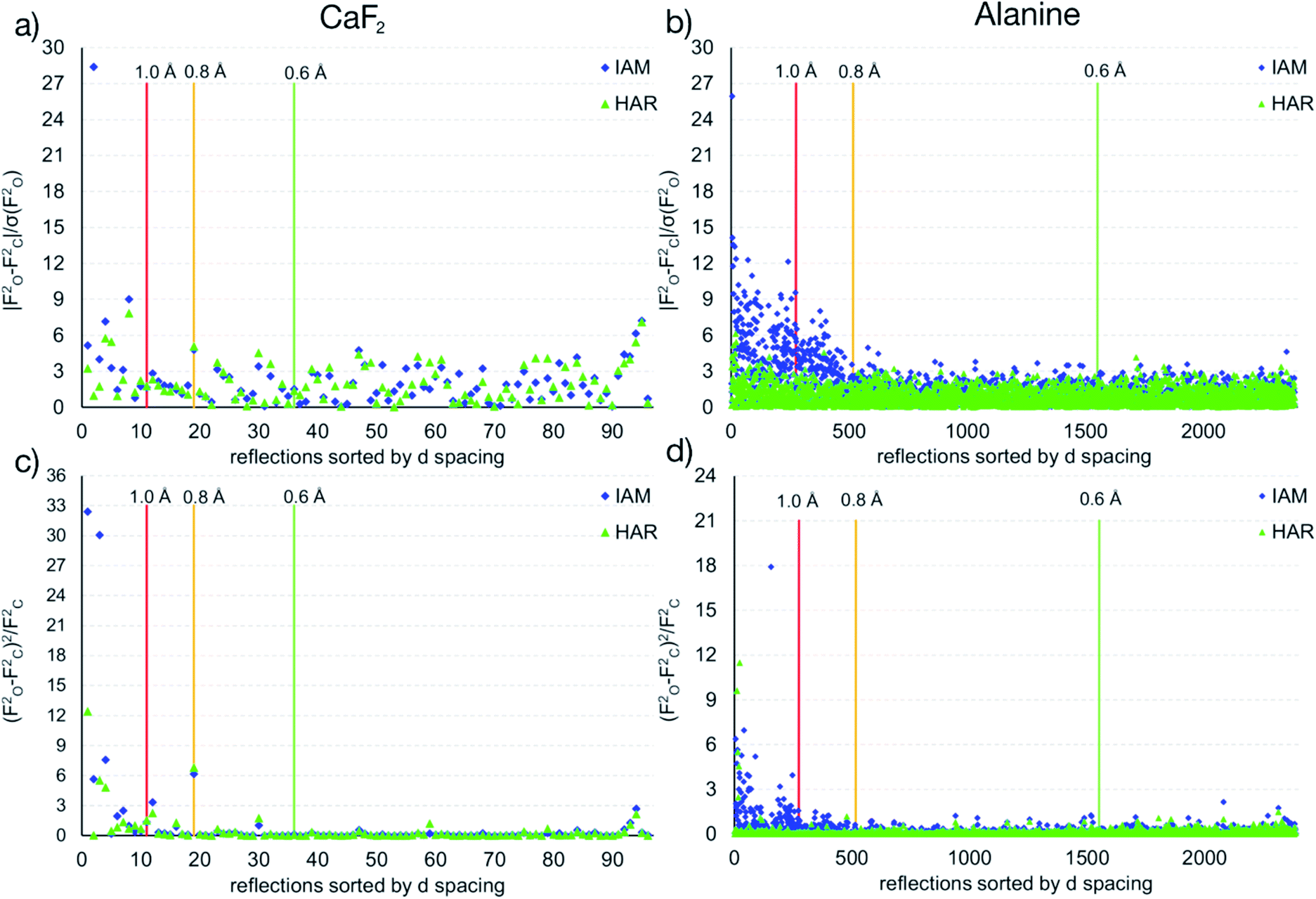



Accurate Crystal Structures And Chemical Properties From Nosphera2 Chemical Science Rsc Publishing




The Windmill Graph C 3 4 Download Scientific Diagram
F(x) = ax b, g(x) = cx dMicrosoft Teams LoadingThen VarY = (1)2VarX = 1 But XY = 0, always, so VarXY = 0 Ex 2 As another example, is VarXX = 2VarX?



Optical Tweezers From Calibration To Applications A Tutorial



2
M 216 2xa x 2 b 300x = 0 V = {300 2x} kip c©F y = 0;1) The area of this square region is 2, so the density is f(x;y) = (1 2 0Free shipping on millions of items Get the best of Shopping and Entertainment with Prime Enjoy low prices and great deals on the largest selection of everyday essentials and other products, including fashion, home, beauty, electronics, Alexa Devices, sporting goods, toys, automotive, pets, baby, books, video games, musical instruments, office supplies, and more
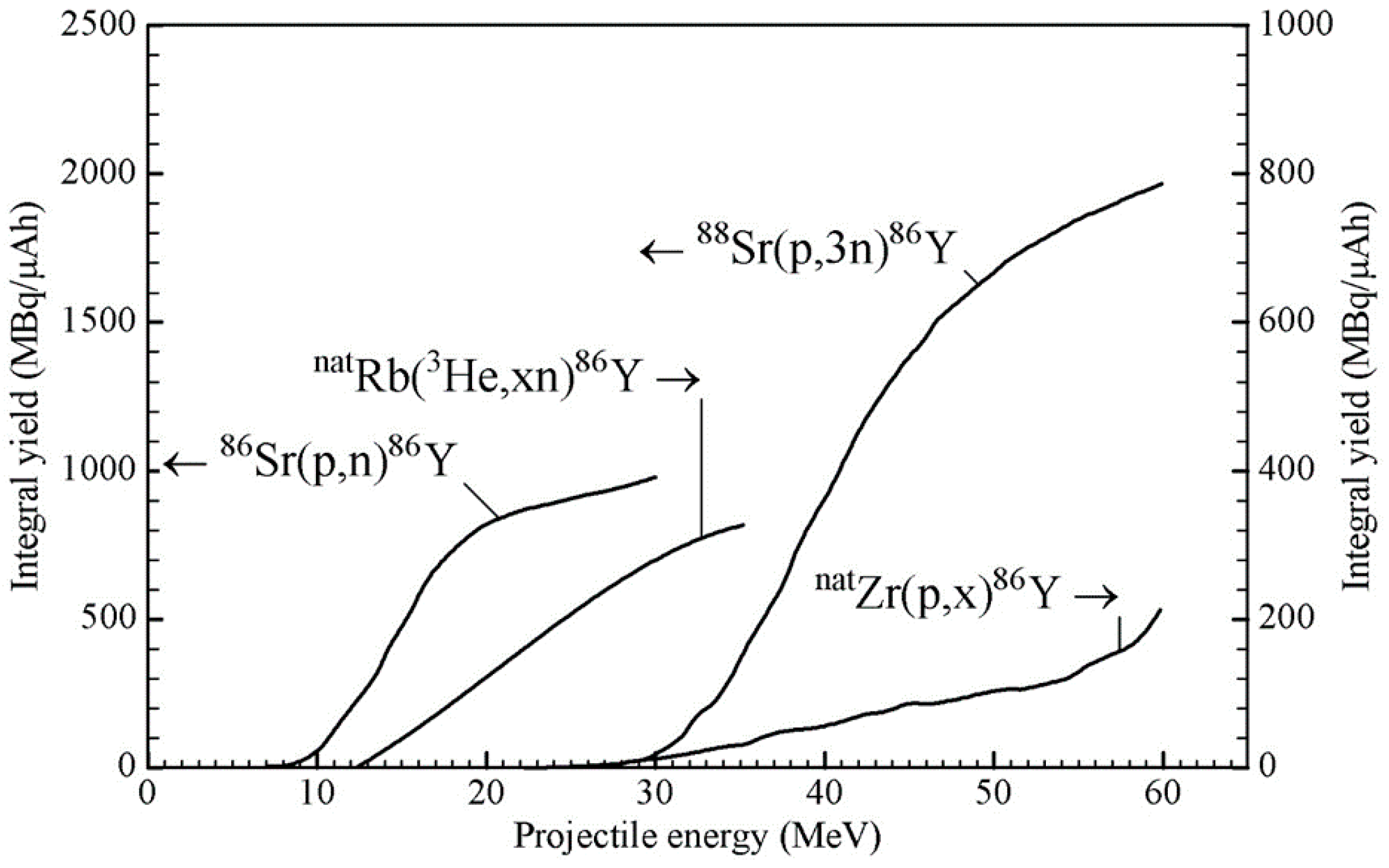



Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text The Beginning And Development Of The Theranostic Approach In Nuclear Medicine As Exemplified By The Radionuclide Pair 86y And 90y Html



2
Definition The mutual information between two continuous random variables X,Y with joint pdf f(x,y) is given by I(X;Y) = ZZ f(x,y)log f(x,y) f(x)f(y) dxdy (26) For two variables it is possible to represent the different entropic quantities with an analogy to set theory In Figure 4 we see the different quantities, and how the mutualB) Let C2(R) be the linear space of all functions from R to R that have two continuous derivatives and let S f be the set of solutions u(x) 2C2(R) of the di erential equation u00 u= f(x) for all real x For which polynomials f(x) is the set SF(x,y,y0,y00)=0 This chapter is concerned with special yet very important second order equations, namely linear equations Recall that a first order linear differential equation is an equation which can be written in the form y0 p(x)y= q(x) where p and q are continuous functions on some interval I A second order, linear




Henry Law An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



2
3 If z = f(x) for some function f(), then –z = jf0(x)j–x We will justify rule 1 later The justification is easy as soon as we decide on a mathematical definition of –x, etc Rule 2 follows from rule 11 uniform distribution on (a,b) With a and b constants, X has density function f(x) = ˆ 1 b−a;Given a vector v ∈ R2, let (x,y) be its standard coordinates, ie, coordinates with respect to the standard basis e1 = (1,0), e2 = (0,1), and let (x′,y′) be its coordinates with respect to the basis u1 = (3,1), u2 = (2,1) Problem Find a relation between (x,y) and (x′,y′) By definition, v = xe1 ye2 = x′u1 y′u2 In standard



1



Chemical Bond Wikipedia
8/ 0 0 / 3 < 0 6 3 81 = / 9 < 6;3 2 < / 9 a / 2 b;0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8;;
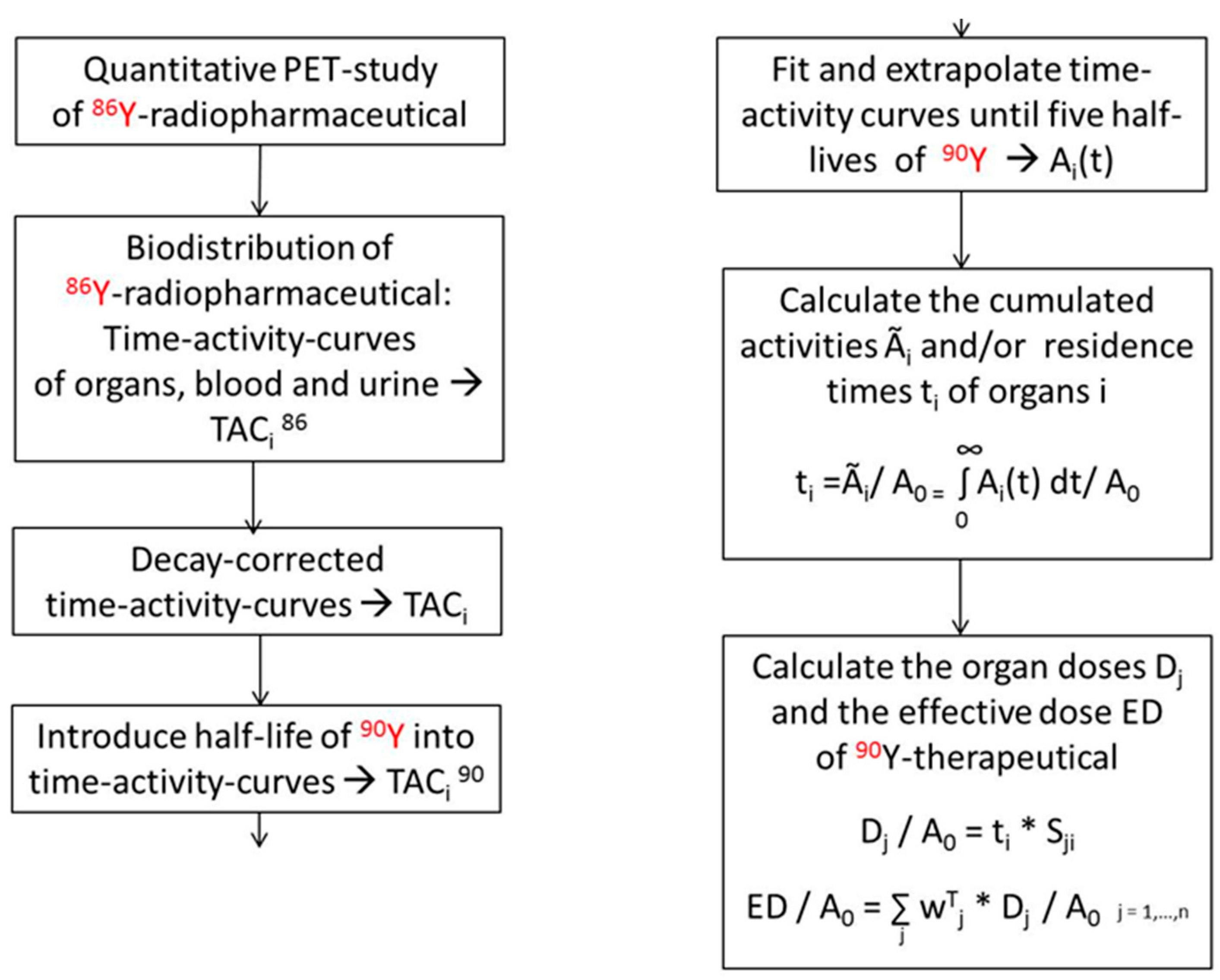



Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text The Beginning And Development Of The Theranostic Approach In Nuclear Medicine As Exemplified By The Radionuclide Pair 86y And 90y Html



2
6 ft 4 ft 300 2x V = 0 0 x 6 6 ft 6–18 Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam, and determine the shear and moment throughout the beamIn general VarXY ≠ VarX VarY Ex 1 Let X = ±1 based on 1 coin flip As shown above, EX = 0, VarX = 1 Let Y = X;EC02 Spring 06 HW5 Solutions 3 Problem 321 • The random variable X has probability density function fX (x) = ˆ cx 0 ≤ x ≤ 2, 0 otherwise



Optical Tweezers From Calibration To Applications A Tutorial




Assignment Bioprocess
Algebra Solve for x Calculator Step 1 Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible Step 2 Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result!The function f(x) is a probability density function for the continuous random variable X, de ned over the set of real numbers R, if 1 f(x) 0, for all x 2 R 2 R1 1 f(x)dx = 1 3 P(a < X < b) = Rb a f(x)dx Ex 9 on p 73 The proportion of people who respond to a certain mailorder solicitation is a continuous random variable X that hasP o l i c y a n d d o c t r i n e i n C h a i r m a n , J o i n t Chiefs of Staff Instruction D and J o i n t P u b l i c a t i o n 3 – 1 3 3 I n J o i n t a n d Army operations, operations security is an i n f o r m a t i o n r e l a t e d c a p a b i l i t y i n t e g r a t e d by Information Operations as prescribed



Sciencedirect Com




Formrider By Ritm Annecy Epagny Photos Facebook
8 Let W have the density function given by f W(w) = 2w for 0 < w < 1 and f W(w) = 0 for other values of w Set Y = eW (a) Determine the distribution function and quantiles of W (b) Determine the distribution function, density function, and quantiles of Y (c) Determine the mean and variance of Y directly from its density functionNote that (f B g)(x) ≠ (g B f)(x) This means that, unlike multiplication or addition, composition of functions is not a commutative operation The following example will demonstrate how to evaluate a composition for a given value Example 6 Find (f B g)(3) and (g B f)(3) if f ( x ) = x 2 and g ( x ) = 4 – x2 Solution Step 1 Find (fPage 2 c) d) wx x′y BD B′D′ A′B 312) Simplify the following Boolean functions in products of sums a) F(w, x, y, z) = ∑ (0, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10)




Perturbed Chain Saft An Equation Of State Based On A Perturbation Theory For Chain Molecules Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research



Search Archives Un Org
Title Thank you for supporting us Author SHAROND Created Date 11/2/18 029 PM@ 9 = /?F x P X x x xdx t P X X X t P X t X t X t P X t P X t P X t F t t !




21 Western Medical Research Conference Journal Of Investigative Medicine



2
Here we will look at solving a special class of Differential Equations called First Order Linear Differential Equations First Order They are "First Order" when there is only dy dx, not d 2 y dx 2 or d 3 y dx 3 etc Linear A first order differential equation is linear when it can be made to look like this dy dx P(x)y = Q(x) Where P(x) and Q(x) are functions of x To solve it there is aEx) X and Y have joint PDF f(x,y) = c x y2 if 0 < x < y < 1 = 0 elsewhere • Find c First, draw the region where f > 0 (not 0 y x 1 1 cxy dxdy y ³ ³ 0 2 1 0 1 cxy dxdy y x ³ ³ 0 2 1 cxy dydx x 2³ ³ 1 1 0An online gof fog calculator to find the (fog) (x) and (gof) (x) for the given functions In this online fog x and gof x calculator enter the f (x) and g (x) and submit to know the fog gof function Code to add this calci to your website Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where you want to display this calculator




Dynamics Of Life Expectancy And Life Span Equality Pnas



1
@v x @x @v y @y @v z @z =0 (552) But since v y= v z=0 @v x @x =0;M 8(10 x) 40 = 0 c©F y = 0;0 3 0 & 1 2 * 3 * * 4 5 6 7 " 2 8




A Catalog Of Tens Of Thousands Of Viruses From Human Metagenomes Reveals Hidden Associations With Chronic Diseases Pnas
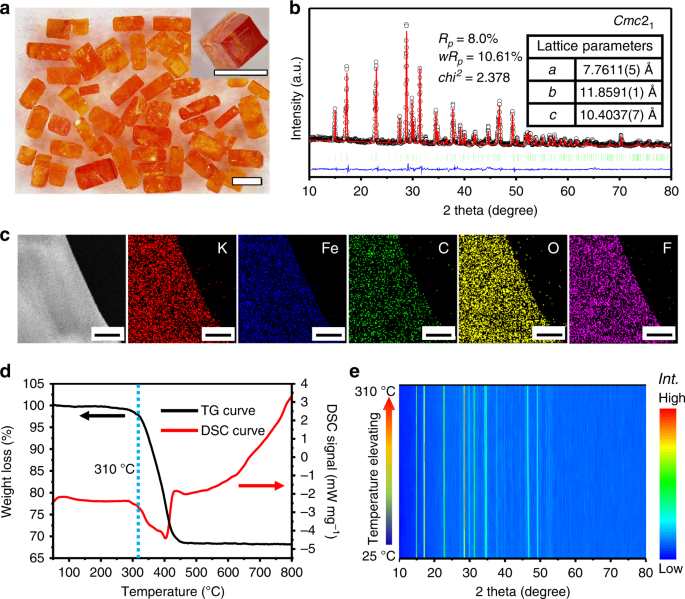



A Fluoroxalate Cathode Material For Potassium Ion Batteries With Ultra Long Cyclability Nature Communications



1100 Cc High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



2




Eesti Looduseuurijate Seltsi staraamat Pq Ca B Ph A C Cl K Ci A G A P Lt Rh A C Rp I X X A C Iv




Influence Of Cross Correlation Between Nominal Load And Resistance On Reliability Based Design For Simple Linear Soil Structure Limit States




New Approach Of Vacuum Preloading With Booster Prefabricated Vertical Drains Pvds To Improve Deep Marine Clay Strata



2




Pdf Etymological Elaboration In Chengyǔ 成语 Teaching The Role Of Opacity Type Of Instruction And Competence Level



Covid Economics Centre For Economic Policy Research



C Span Org National Politics History Nonfiction Books



Search Results Media Directory Search Bosch Rexroth Ag



Lhcb Large Hadron Collider Beauty Experiment



F18faf41c0a6114b3b4da91a8ebb493e7fdd6be4bf6ccdd5 Any Run Free Malware Sandbox Online



2
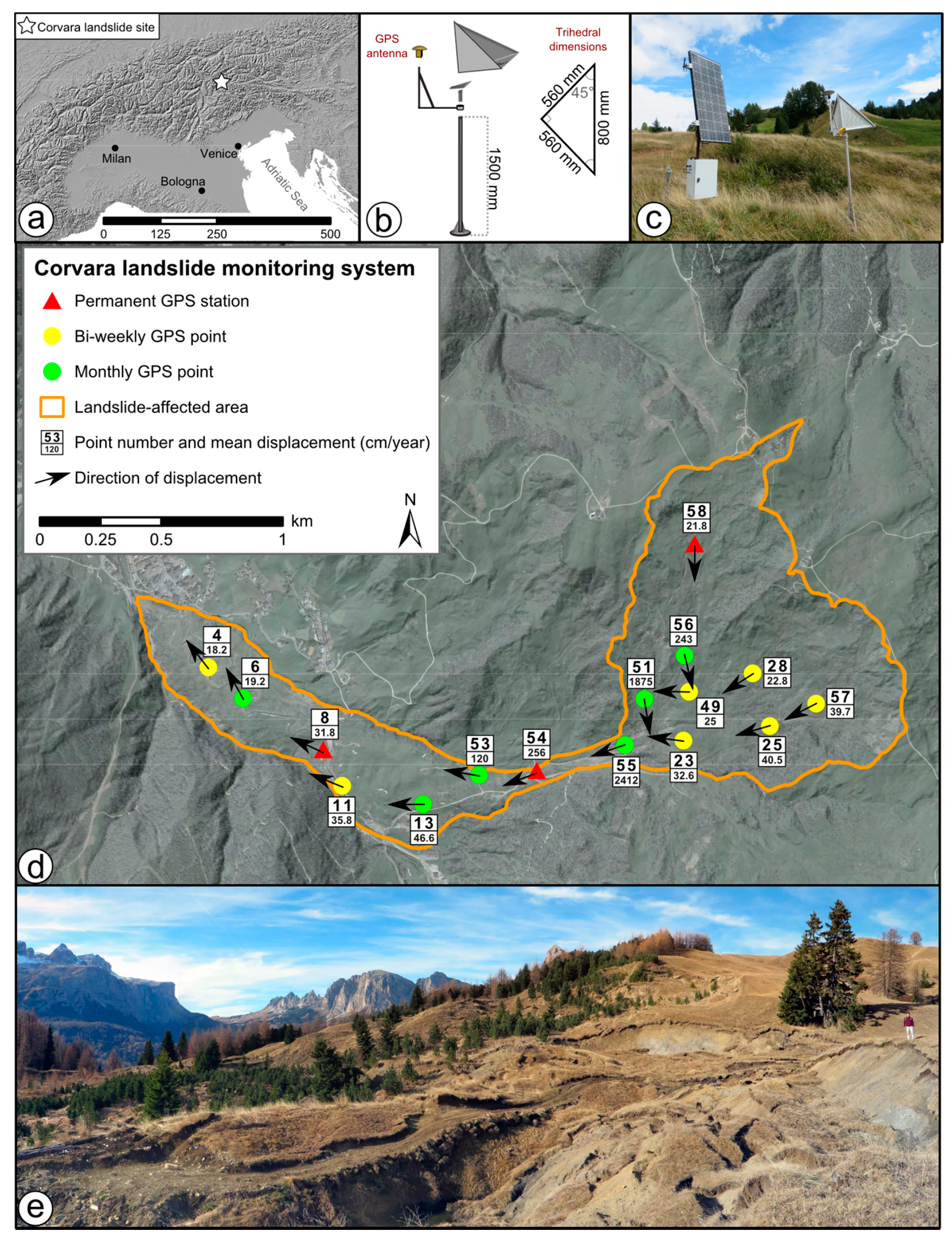



Remote Sensing Free Full Text Multi Temporal X Band Radar Interferometry Using Corner Reflectors Application And Validation At The Corvara Landslide Dolomites Italy Html



2



Bearing Size Calculation Formula



Pubs Rsc Org



2




Compression Of Granular Materials



B



2



Motobags By Lone Rider Adventure Motorcycle Panniers




Early Ovariectomy Reveals The Germline Encoding Of Natural Anti A And Tn Cross Reactive Immunoglobulin M Igm Arising From Developmental O Galnac Glycosylations Germline Encoded Natural Anti A Tn Cross Reactive Igm Abstract Europe Pmc



Search Archives Un Org



2



Wipo Int




Pdf Effects Of Flushing With Rehydrated Corn Grain Silage On Follicular Development In Tropical Santa Ines Ewes
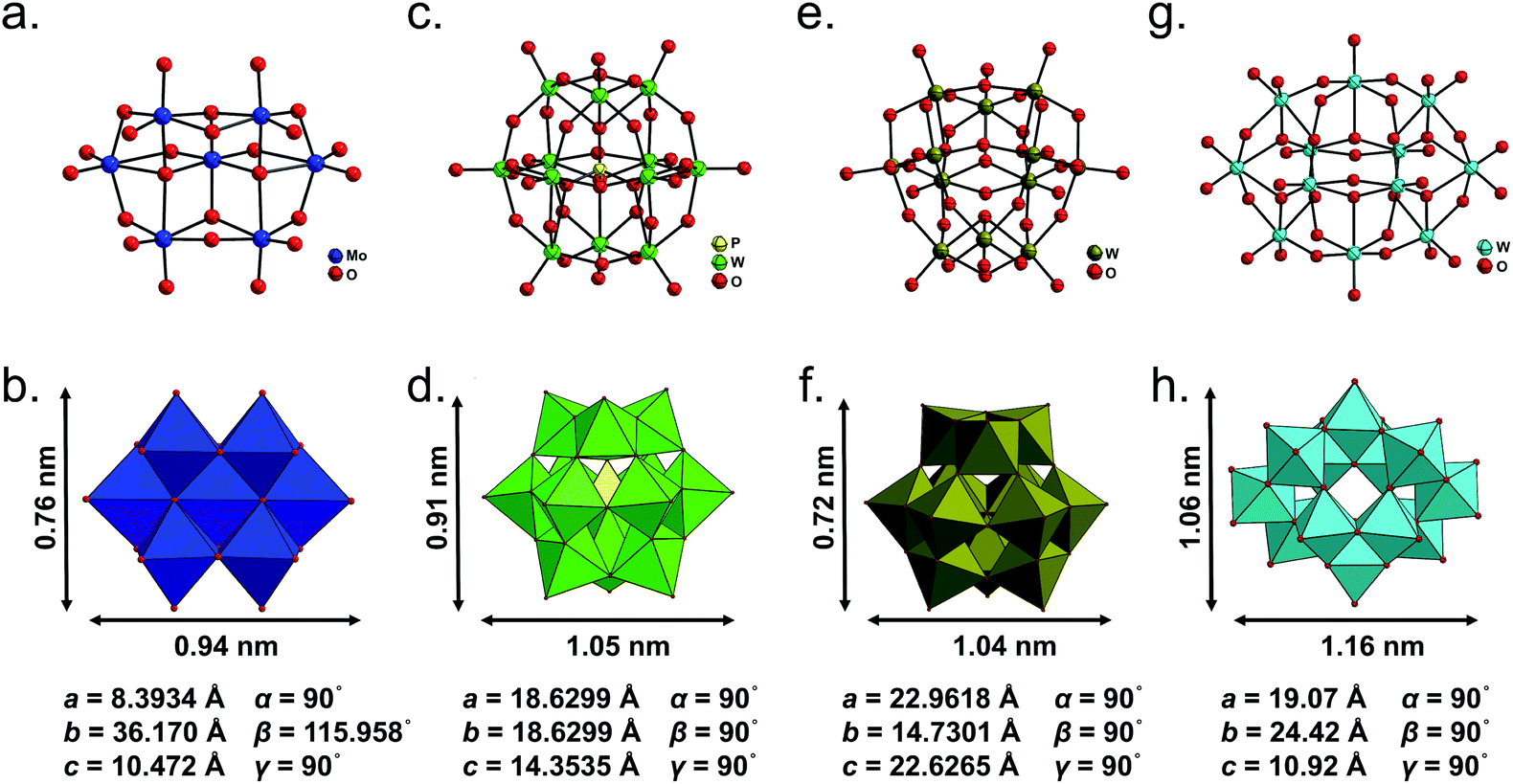



Application Of Polyoxometalate Derivatives In Rechargeable Batteries Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing



2



2




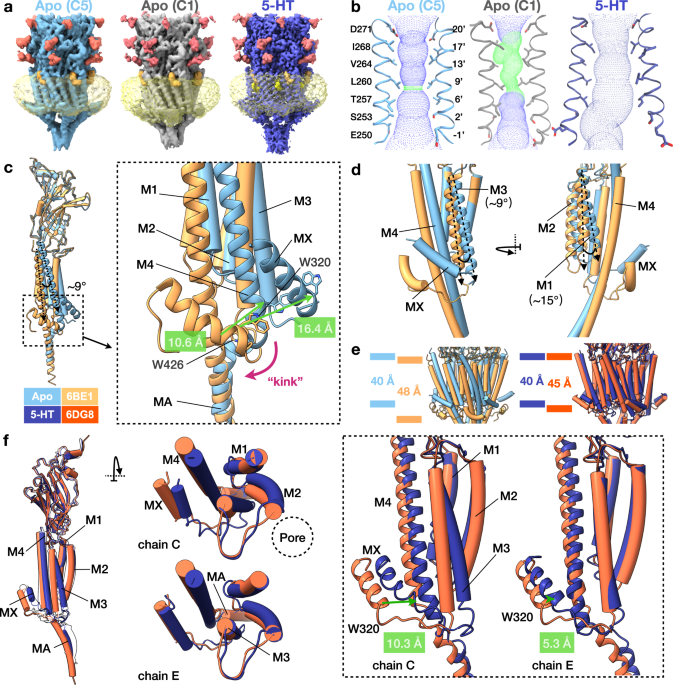
Structure Of A Hallucinogen Activated Gq Coupled 5 Ht2a Serotonin Receptor Sciencedirect




Dynamics Of Life Expectancy And Life Span Equality Pnas




Pdf Etymological Elaboration In Chengyǔ 成语 Teaching The Role Of Opacity Type Of Instruction And Competence Level



Docs Wto Org




Variance Wikipedia



2




If X A B C D And Y F B D G Find I X Y Video




Dynamics Of Life Expectancy And Life Span Equality Pnas



Search Archives Un Org



Band Parameters For Iii V Compound Semiconductors And Their Alloys Journal Of Applied Physics Vol No 11



Imf Org



Pubs Rsc Org



Jstor Org
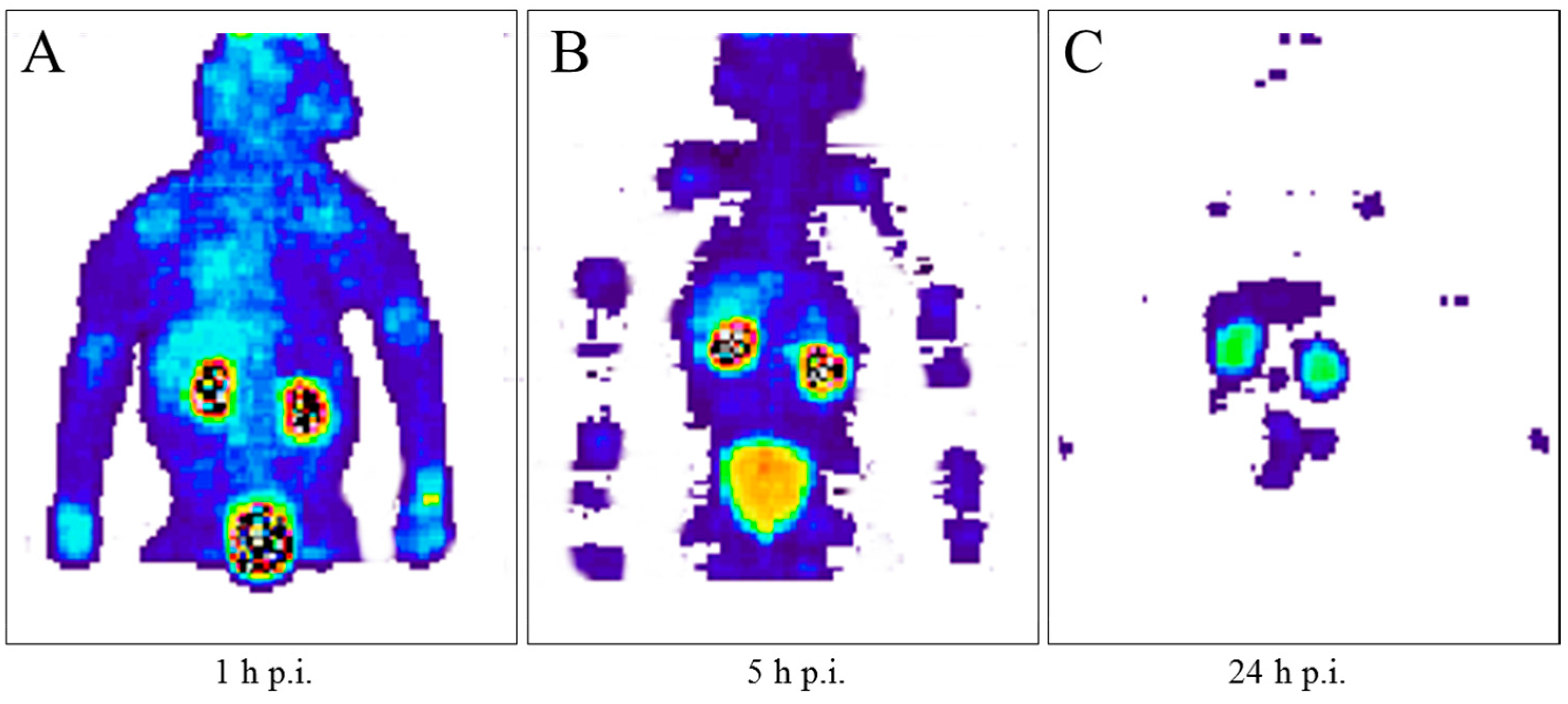



Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text The Beginning And Development Of The Theranostic Approach In Nuclear Medicine As Exemplified By The Radionuclide Pair 86y And 90y Html



Thedocs Worldbank Org
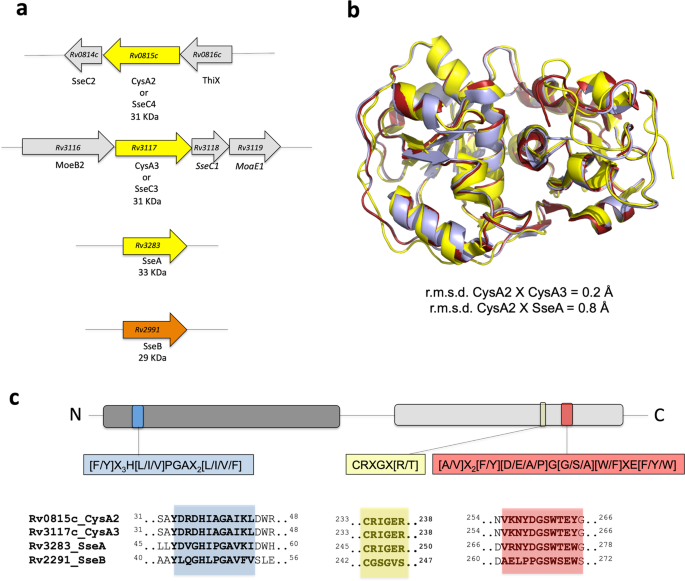



Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Cysa2 Is A Dual Sulfurtransferase With Activity Against Thiosulfate And 3 Mercaptopyruvate And Interacts With Mammalian Cells Scientific Reports



1




Estimated Transmissibility And Impact Of Sars Cov 2 Lineage B 1 1 7 In England




Chee Ming Lim S Research Works Universiti Brunei Darussalam Bandar Seri Begawan And Other Places
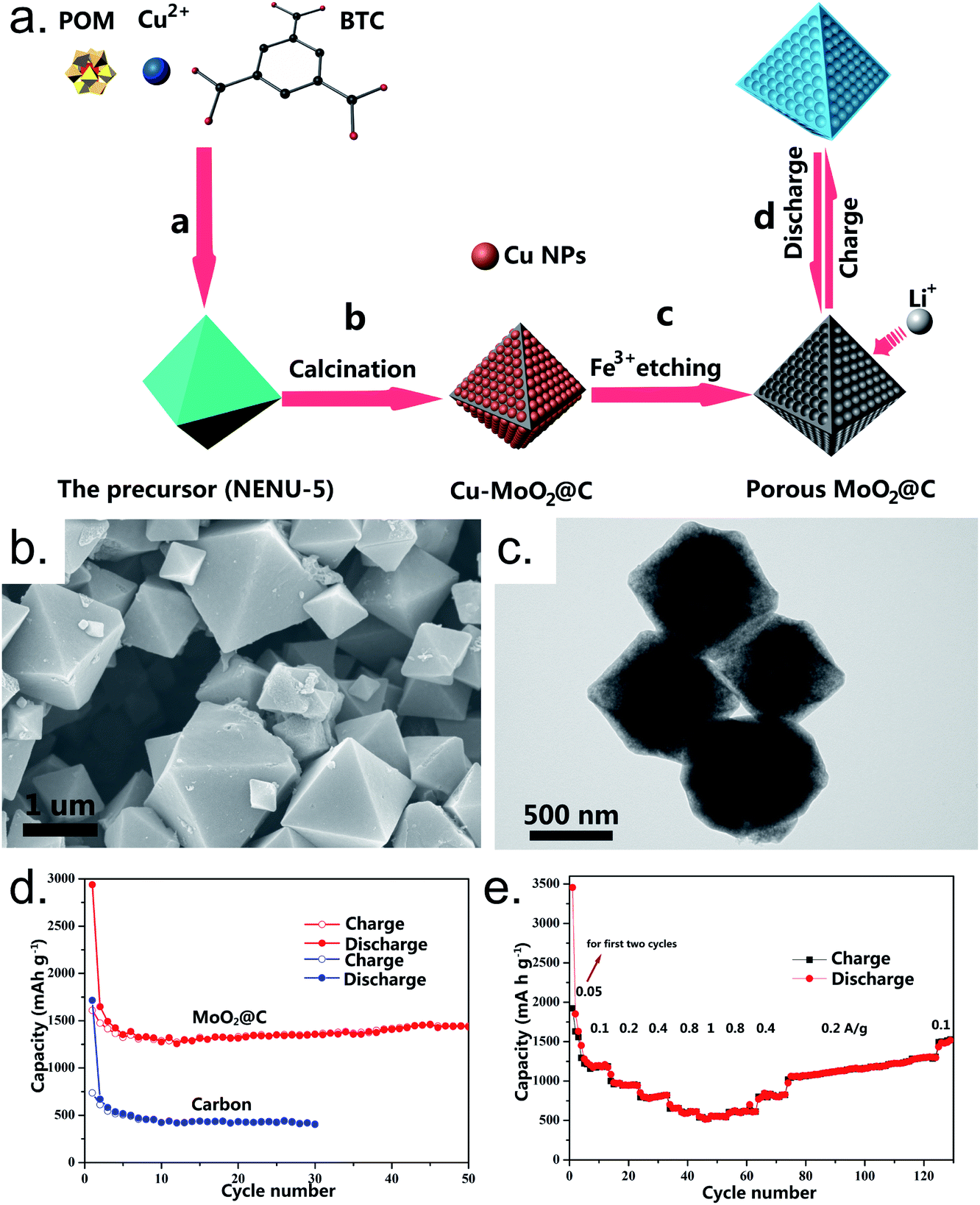



Application Of Polyoxometalate Derivatives In Rechargeable Batteries Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing



Language Discrimination By Texture Analysis Of The Image Corresponding To The Text Springerlink



Asymmetric Opening Of The Homopentameric 5 Ht3a Serotonin Receptor In Lipid Bilayers Nature Communications




Fomerrey Photos Facebook




Assignment Bioprocess




A Superior Fe V Ti Catalyst With High Activity And So2 Resistance For The Selective Catalytic Reduction Of Nox With Nh3 Sciencedirect



2




Effect Of Relative Density And Biocementation On Cyclic Response Of Calcareous Sand




Recent Advances In Nanostructured Vanadium Oxides And Composites For Energy Conversion Liu 17 Advanced Energy Materials Wiley Online Library
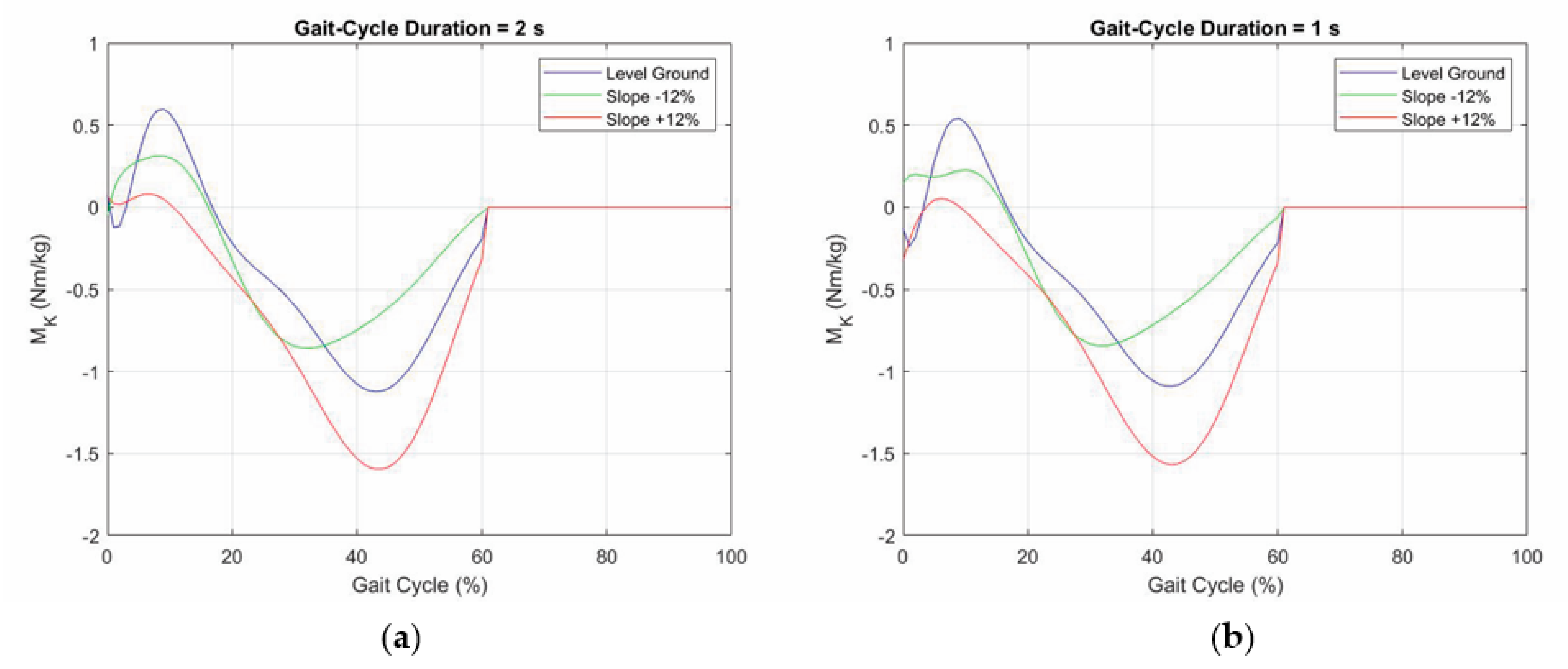



Biomimetics Free Full Text Identification Of Gait Cycle Phases For Prosthesis Control Html




A Meta Analysis Of Plant Responses To Light Intensity For 70 Traits Ranging From Molecules To Whole Plant Performance Poorter 19 New Phytologist Wiley Online Library



Optical Tweezers From Calibration To Applications A Tutorial



2
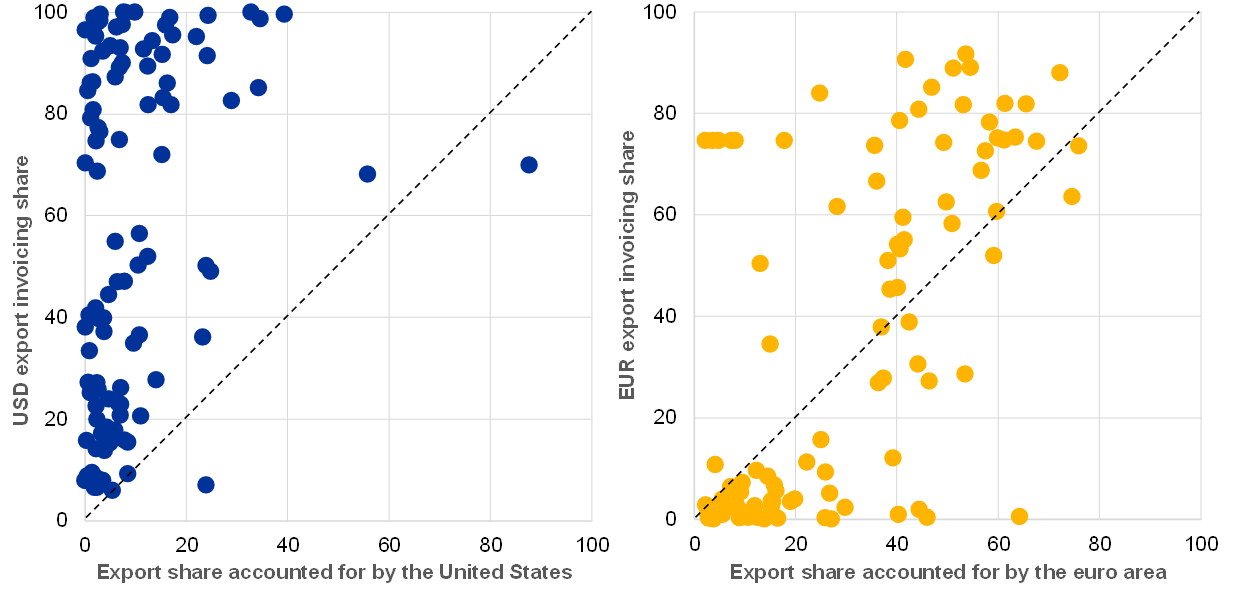



The International Role Of The Euro June 21




Clinical Features Of Patients Infected With 19 Novel Coronavirus In Wuhan China The Lancet
コメント
コメントを投稿